Doctors Without Borders joins noma survivors in celebrating inclusion in WHO neglected tropical diseases list
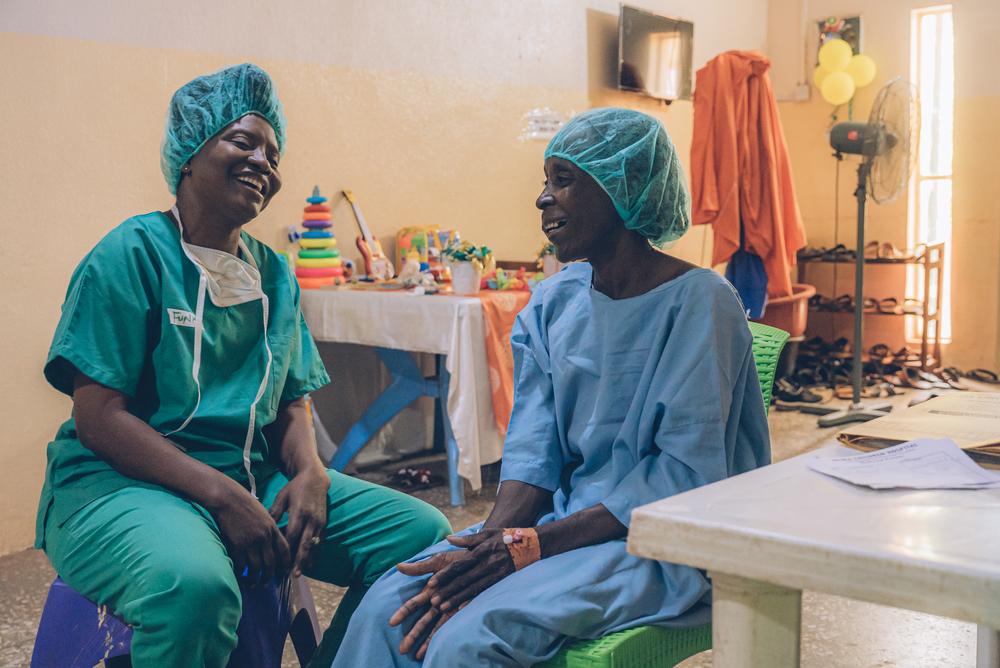
Doctors Without Borders counsellor from the mental health department, talks to a Noma survivor from Yobe state, before her surgery. Nigeria, May 2023. © Fabrice Caterini/Inediz
Amsterdam – Three years into its campaign to have noma recognised as a neglected tropical disease (NTD), international medical organisation Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF) welcomes the decision by Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, director-general of the World Health Organization (WHO), to include noma in the WHO’s official list of NTDs.
Following a meeting in Geneva on 12 October, the Strategic and Technical Advisory Group for Neglected Tropical Diseases (STAG-NTD) concluded that noma fits all the criteria for inclusion on the WHO’s official list. The group shared this recommendation with the WHO director-general, who has now ratified it.
We welcome the WHO director-general’s decision, which confirms what Doctors Without Borders and the medical community have insisted on for years: that noma is a neglected tropical disease and deserves all the attention and resources that this implies. We hope that this decision will shine a spotlight on the disease, facilitating the integration of noma prevention and treatment activities into existing public health programmes, and encouraging the allocation of much-needed resources to help tackle the disease.Mark Sherlock, health programmes manager
Noma is a completely preventable disease and is easy to treat if addressed in time. Untreated, it destroys the skin and bones of the face in just a few weeks, leading to death for around 90 per cent of those infected. The 10 per cent who survive face a future of pain, disfigurement and social stigma. The disease most commonly affects children who are malnourished or whose immune systems are otherwise compromised.
The lead sponsor country for the request to have noma recognised as an NTD is Nigeria. In January 2023, the Nigerian Ministry of Health submitted a package to the WHO which included an official request letter, letters of endorsement from 31 countries, and a dossier of evidence demonstrating that noma fits the criteria for inclusion. Doctors Without Borders supported Nigeria in providing the medical evidence, based on years of research and drawing on Doctors Without Borders’s experience treating survivors of noma, in the hope that NTD listing will bring increased attention, earlier diagnosis and stronger research.
Doctors Without Borders has supported the Nigerian Ministry of Health’s Sokoto noma hospital, in northwest Nigeria, since 2014, where its teams provide reconstructive surgery, nutritional support, mental health support and outreach activities. Since 2014, Doctors Without Borders’s surgical teams in Sokoto have carried out 1,203 surgeries on 837 patients.
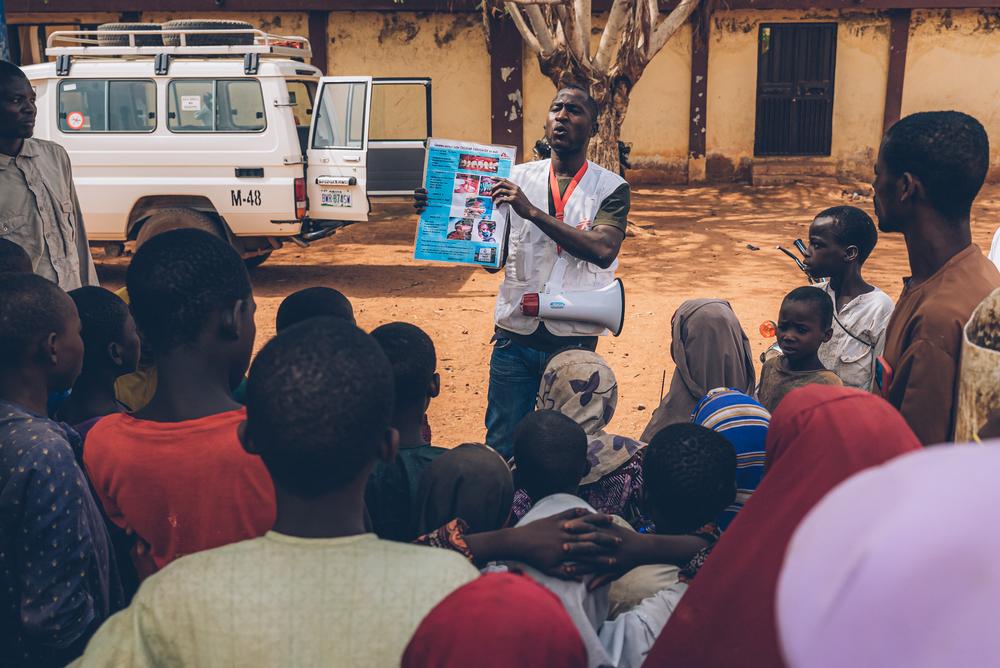

The outreach team of the Noma Hospital in Sokoto, Nigeria, started in January 2017 active case finding in Sokoto state. Here, in Sayinna village, the team is showing leaflets to check if someone identifies a noma case in the area. Nigeria, May 2023. © Fabrice Caterini/Inediz
Inclusion in the WHO’s list of NTDs is an important step, but not the final one. We plan to shift towards mobilising resources and strategic alliances within the global health community to facilitate programming and research to raise awareness of noma, reduce mortality and improve the patients and survivors' life conditions.Mark Sherlock, health programmes manager
Doctors Without Borders plans to focus on research, expanding its collaboration with academic institutes around the world to discover more about the causes of noma. Another key step will be to integrate noma surveillance systems into Doctors Without Borders’s medical work. “In endemic countries, Doctors Without Borders plans to introduce screening for noma into existing Doctors Without Borders programmes, such as malnutrition screening and vaccination campaigns, with the aim of early detection and prompt treatment,” says Sherlock.
Finally, Doctors Without Borders will continue its advocacy efforts around noma. Its three-year campaign has received strong support from survivors of the disease, who have contributed their voices to get across the simple but important message: that noma is a preventable and treatable disease which should no longer exist.
Doctors Without Borders has supported the Nigerian Ministry of Health’s Sokoto Noma Hospital since 2014, providing reconstructive surgery, nutritional support, mental health support and outreach activities. Since 2014, Doctors Without Borders’s surgical teams have carried out 1,260 surgeries on 882 patients. All services at Sokoto noma hospital are provided free of charge.
