Burkina Faso: Providing healthcare in a region ravaged by violence
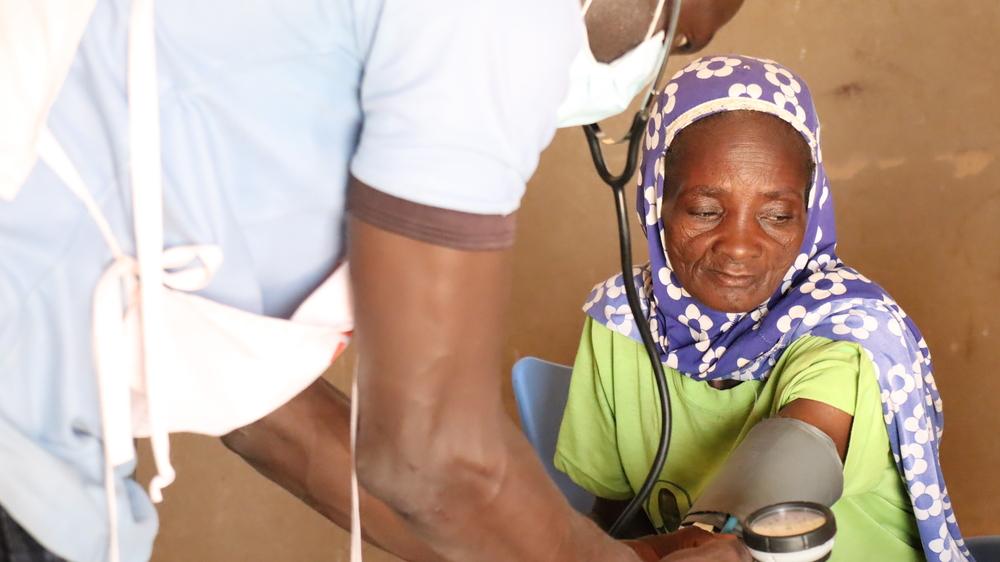

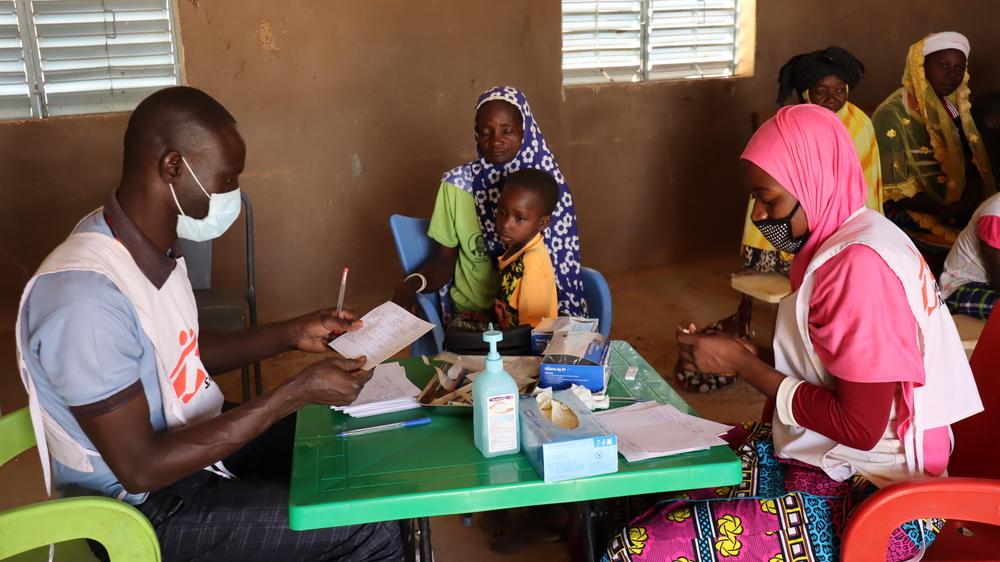
Mariam and her child visiting MSF’s mobile clinic in Sirfou, a village in Burkina Faso’s North region. "I’m here with my sick child. We both are sick, and the free services are such a relief," says Mariam. Since they fled their hometown, Mariam has been finding it difficult to access healthcare, either due to the absence of the services or due to financial barriers. This is Mariam’s first visit to Doctors Without Borders mobile clinics. February 2021 © Noelie Sawadogo/MSF
Burkina Faso’s North region hosts more than 100,000 internally displaced people who fled recurring violence in this part of the country. Since January 2021, Doctors Without Borders mobile teams have been offering healthcare support to people in the villages of Sirfou, Todiame, Rounga and Ouindigui, where thousands of these displaced persons have settled, but where access to healthcare and other basic services is severely limited.
“We have nothing left, since we fled the conflict. We don’t even have money to pay for treatment,” says Zallé Ramata, a displaced woman living in the village of Sirfou. On this day, Zallè brought two of her children to receive free medical assistance from Doctors Without Borders/Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF), whose teams have been regularly visiting this village since January 2021. “They weren’t feeling well. They spent last night throwing up until the morning,” she says.
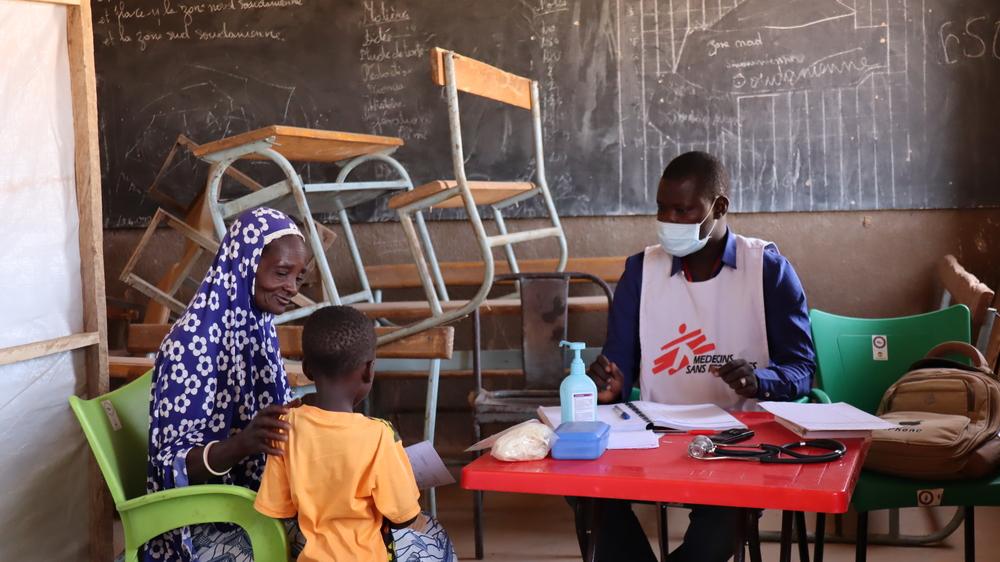

Mariam and her child visiting MSF’s mobile clinic in Sirfou, a village in Burkina Faso’s North region. February 2021 © Noelie Sawadogo/MSF
These “mobile clinics” have been deployed as a complement to Doctors Without Borders medical services in the town of Titao, to provide free healthcare in an area where thousands of displaced people have settled, fleeing a cycle of violence that for years has pitted armed groups against the military, as well as intercommunal clashes.
Out of 23 health centres in the district of Titao, 15 are not operating at full capacity and another three are shut down due to the conflict. This adds to the difficulty in movement due to long distances, the insecurity and the lack of means of transportation, making access to basic health services in Titao’s district almost impossible. Doctors Without Borders mobile teams regularly visit Sirfou and the neighbouring villages of Todiame, Rounga and Ouindigui.
These villages are located several kilometres from the nearest health centre. In Sirfou for example, where we are today, the nearest health centre is seven kilometres away. The majority of the displaced persons have neither the means of transportation nor the money to get there. Our main objective is to provide healthcare services to both displaced people and host communities that have no access to them and already suffered a lot because of the widespread violence.”Monique Diarra, nurse
February 2021 © Noelie Sawadogo/MSF
Every week, a Doctors Without Borders team of five travels several dozen kilometres to reach these villages, often on very poor roads. The journey is relatively easier in the dry season, but becomes longer and more difficult when the rain start falling. The region’s chronic insecurity adds to the difficulties in the movements; it took months for the conditions to allow Doctors Without Borders teams to leave the town of Titao and reach these villages in the outskirts.
“We provide primary healthcare services that include treatment for common diseases such as malaria, diarrhoea and respiratory infections. Recently, we started providing treatment for chronic diseases and mental health support,” says Diarra.
Between January and March 2021, Doctors Without Borders provided more than 1,600 medical consultations to host and displaced communities in an area where around 15,000 people live.
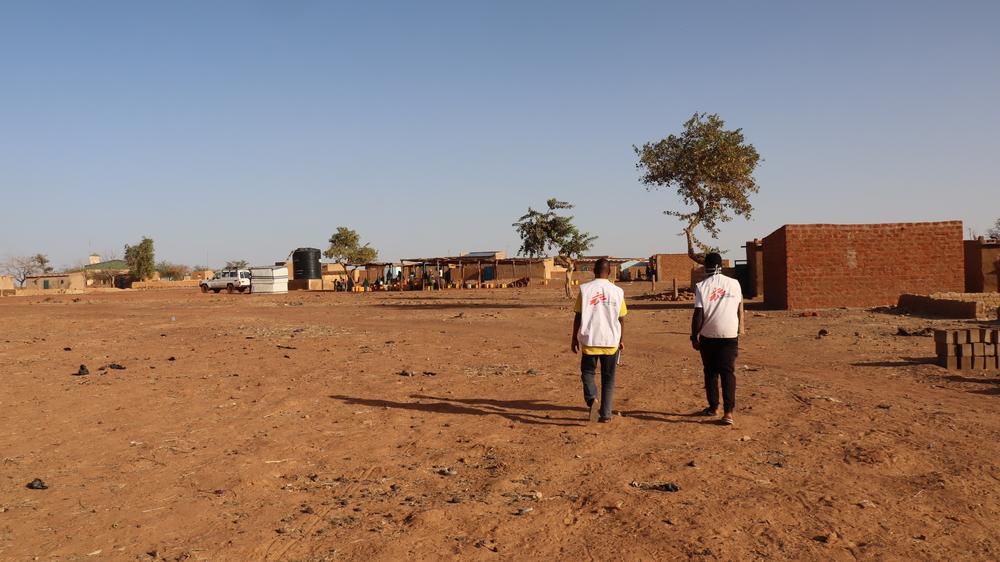

MSF teams visiting a newly rehabilitated borehole in the town of Titao in Burkina Faso’s North region. February 2021 © Noelie Sawadogo/MSF
By the end of 2020, many displaced people that had settled in Titao decided to come back to their area of origin but the local health centres are still closed.
With the rain and the peak of malaria season approaching, Doctors Without Borders teams are concerned about the likely increase in people’s needs in a remote area with few services available. The risk of malaria is higher because mosquitoes reproduce in stagnant water.
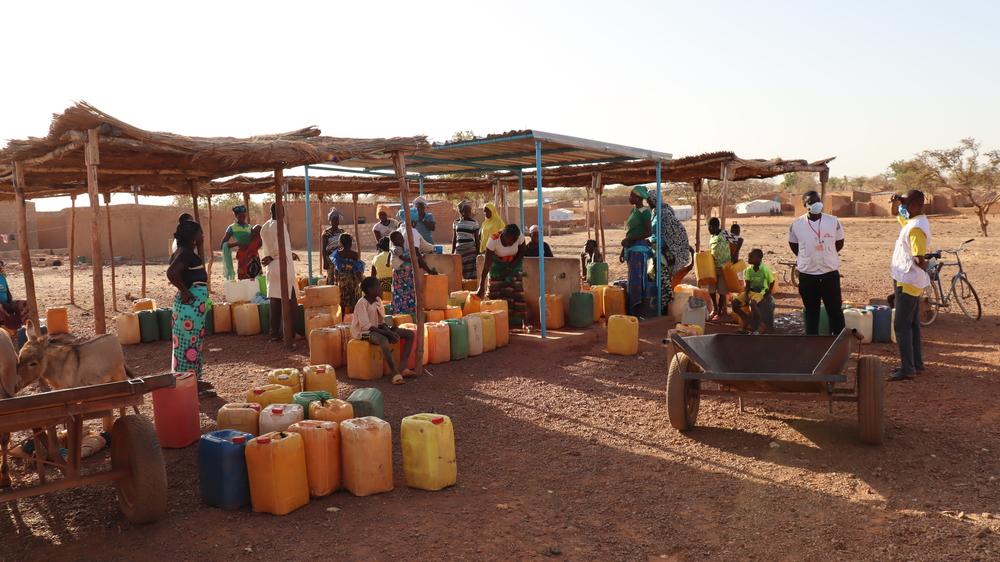

Women and children filling their jerry cans with clean water at a newly rehabilitated borehole in the town in Titao in Burkina Faso’s North region. The lack of clean water can cause different parasitic infections and other water-borne diseases such as cholera and diarrhoea. February 2021 © Noelie Sawadogo/MSF
“Our medical work base in Titao is a short-term solution we launched this year to respond to the needs of people who were recently displaced,” says Dr Diallo Alpha Amadou, Doctors Without Borders medical coordinator in Burkina Faso. Doctors Without Borders teams also support five health facilities in the district of Titao to help them regain their full working capacity, as a more long-term solution. “When these health centres are ready to admit patients again, we will move our mobile clinics towards other villages,” says Dr Alpha. Doctors Without Borders medical teams also support local health authorities with mass vaccination campaigns against common diseases among the displaced population.
Doctors Without Borders logistics teams rehabilitate old boreholes or build new ones to increase access to clean water. With the waves of displacements, poor living conditions for displaced people and the lack of clean water, diseases can easily spread.
“We receive many patients suffering from diseases they caught by drinking polluted or dirty water. In many areas in the North region, just like in other areas of the country where displaced people settled, access to clean water remains a challenge for thousands. The lack of water access points and their bad quality are reasons behind different parasitic infections and other water-borne diseases such as cholera and diarrhoea,” says Dr Alpha.

